If you have a business that drives a significant amount of new business via search engines, odds are you’ve felt the impact of AI in SEO in some form or another.
As we noted in a previous article, AI Overviews continues to become a bigger part of Google’s search experience. Since then Google has also announced its AI Mode, a new Gemini-powered experience that will allow searchers to ask questions, do research, and guide them towards products and services, and competitors are working on similar iterations on their core search engine experience. Additionally, there are popular chat agent platforms like ChatGPT, Gemini, and Claude that an increasing number of users are using as search engines with more conversational-style responses.
To help with this increasingly complex aspect of search, we’ll break it down into two general categories, and share a core list of SEO best practices that will go a long way towards increasing your brand’s AI preparedness.
What is AI in SEO?
AI-generated elements in the search engine
We’ve talked about Google AI Overviews at length before. AIO is the biggest example of generative copy appearing as part of a standard search engine experience. In that sense, AIO is an additive part of the standard searches people have been making since the start of search engines.
In contrast, there’s a parallel trend developing, where some search behavior is migrating away from traditional search engines.
AI chatbots as the search engine
Some users have begun to take the open-ended format of web hosted chat agents like ChatGPT, Gemini, and Claude and input questions that, historically, they would have directed towards a search engine like Google. While the responses generated to certain queries will, similar to an Overview, produce a summarized article-like response, included in certain responses are links back to third party sites around the Web, typically as attribution for certain information being cited in the generative write up. These outlinks have the potential to be a source of new inbound traffic and conversions for brands that get cited frequently in response to commercially relevant chat queries.
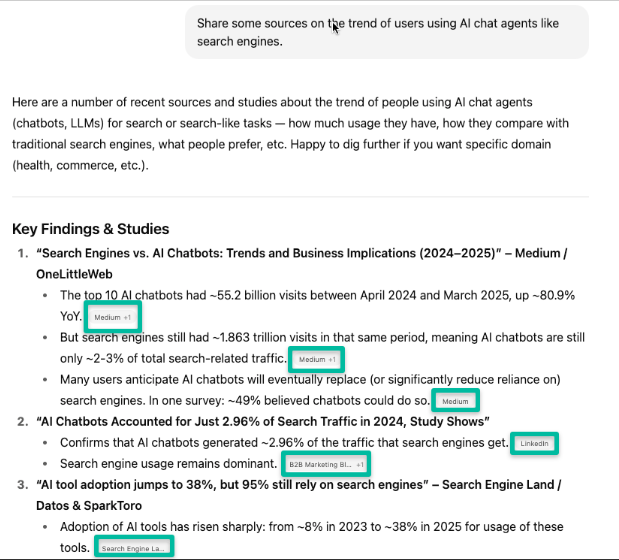
It’s important to note that as of 2025, search traffic still flows primarily through traditional engines. A recent study by SparkToro found that Google search is still 210x bigger than ChatGPT in terms of sheer amount of daily searches. But the rise of AI-first discovery methods signals a shift in how people will engage with brands online. Along with several other industry factors, it could also contribute on some level to increased competition in the search landscape, with 2025 being the first year Google’s share of the search market landscape dropped below 90% in ten years.
Because of all of this, it remains critical to ensure your site is structured and optimized so that AI-powered systems can parse, prioritize, and present your content effectively.
Defining Generative Engine Optimization
Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) is an umbrella term for preparing your content and site structure for AI-driven discovery systems like Google’s AI Overviews and third-party AI chatbots. Similar to traditional SEO work, GEO focuses on content visibility, structured data, and technical performance, but with added emphasis on how large language models (LLMs) extract, interpret, and summarize information.
However, GEO doesn’t exist in isolation. We recommend viewing it as part of a Shared Core; the foundational layer of technical, content, and experience principles that power both GEO and SEO. This includes elements like structured data, internal linking, Core Web Vitals, and schema markup; the connective layer that ensures visibility, crawlability, and authority across human-led and AI-driven discovery. By strengthening this Shared Core, brands create compounding visibility and performance benefits wherever search is happening.
GEO and the Shared Core concept
The criteria for appearing in these emerging types of search elements and platforms is still evolving alongside these SERP elements and platforms themselves. That said, much of what we do know is already in the wheelhouse of good SEO. In a recent interview, Gary Illyes of Google confirmed that brands don’t need a separate "GEO" strategy to appear in AI Overviews. Instead, the ideal approach is normal SEO best practices with a renewed focus on what truly matters: creating high-quality, people-first content that demonstrates authority and is impeccably structured.
This reinforces the Shared Core philosophy: that a brand’s long-term AI preparedness isn’t about layering new tactics on top of fragmented systems, but about strengthening the single, integrated foundation that informs every channel.
With that in mind, here are a few of those SEO initiatives that will position a brand well for AI elements in search.
Core aspects of AI preparedness for SEO
Off-page GEO
- Schema tagging - Use FAQ, HowTo, and Product schemas (along with Article or Local Business where relevant) to make your content more machine-readable and AI-friendly.
- Robots meta tag - Configure index, follow, max-snippet, max-image-preview, max-video-preview directives to control how your content appears in AI Overviews and search results.
On-page GEO
- Content depth & topical authority - Cover topics comprehensively with clear definitions, examples, and references to build authority and improve AI extractability.
- Meta title & description optimization - Keep titles concise, accurate, and aligned with user intent; update descriptions regularly to guide AI-generated snippets.
- Semantic HTML structure - Use clear H2-H4 hierarchies, lists, and definitions in the first 100 words to improve readability for both humans and AI models.
- Direct answer & snippet optimization - Place short, precise answers to common questions in well-labeled sections to increase visibility in AI summaries.
- Multimedia content - Add images, video, and charts with proper metadata so AI systems can surface richer answers across formats.
Technical work
- Page speed & Core Web Vitals - Keep Largest Contentful Paint under 2.5s, First Input Delay under 100ms, and Cumulative Layout Shift under 0.1 to ensure fast, reliable experiences.
- Mobile friendliness - Use responsive design and test across devices to meet Google’s mobile-first indexing standards and AI-driven usability checks.
All of these GEO and SEO principles ladder up to the Shared Core: the central framework of site health, structured data, and content clarity that allows both search engines and AI models to interpret your brand consistently.
SEO, AIO, and GEO together define the future of search visibility. Get a fast read on what’s blocking your brand across all three, and a clear roadmap to capture more clicks, citations, and conversions.
Request a complimentary audit here.
About the Author:
This article was written by Mark Aspillera, Senior SEO Strategist at BMG360. Part SEO strategist, part client whisperer, Mark leads search strategy and client services for a tight roster of high-end national and international brands. From setting the big-picture SEO roadmap to running the day-to-day, he makes sure every tactic maps back to what actually moves the needle. If he's not deep in a rank report or a strategy doc, he's probably on a client call making complex things sound simple.